crm analytics examples showcasing impactful business insights
crm analytics examples sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into practical strategies and game-changing successes that transform customer relationship management into a true driver of business growth.
From understanding customer behaviors and segmenting audiences to accurately forecasting sales and enhancing retention, crm analytics examples highlight how data-driven decisions can reshape marketing, sales, and customer support across diverse industries. By using modern analytical techniques and advanced CRM tools, organizations can unlock actionable insights to personalize experiences, optimize campaigns, and boost long-term value from every customer interaction.
CRM Analytics Examples
CRM analytics refers to the strategies and technologies that businesses use to collect, analyze, and interpret customer data, helping organizations better understand their customers and make informed decisions. As companies compete in increasingly data-driven markets, CRM analytics has become essential in improving customer relationships, driving sales, enhancing service quality, and optimizing marketing efforts.
Modern CRM analytics integrates seamlessly with business operations, enabling personalized engagement, predictive intelligence, and targeted campaign management. These analytics tools empower teams to identify trends, predict customer behaviors, and measure the success of relationship-building strategies, transforming how businesses interact with their customers.
Core Business Areas Transformed by CRM Analytics, Crm analytics examples
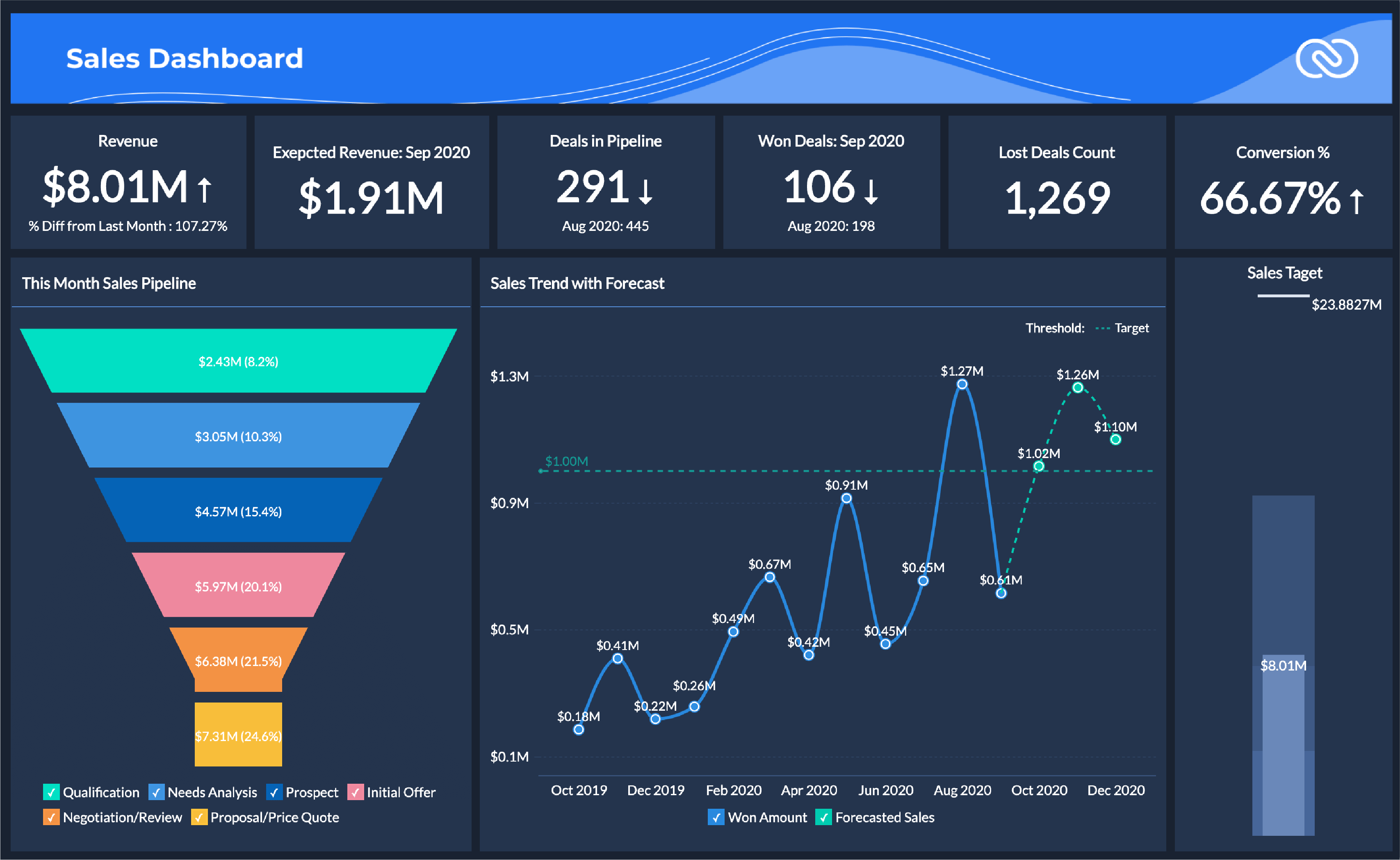
By leveraging CRM analytics, organizations can optimize various business processes across departments. Several key areas commonly see significant improvements:
- Sales pipeline management and forecasting
- Customer segmentation and targeted marketing
- Customer retention and churn reduction
- Campaign performance measurement
- Enhanced customer service response
Types of CRM Analytics
CRM analytics encompasses multiple types of data analysis, each serving a unique function in the customer management lifecycle. Understanding the different forms of analytics can help businesses determine which approach best fits their goals and challenges.
| Type | Purpose | Typical Use Cases | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Descriptive Analytics | Summarizes historical customer data to reveal trends or patterns. | Sales reports, customer demographic analysis, campaign summaries. | Improved understanding of past performance and customer behaviors. |
| Diagnostic Analytics | Identifies causes behind certain outcomes or patterns. | Root cause analysis for churn, evaluating failed campaigns. | Pinpoints problem areas and opportunities for improvement. |
| Predictive Analytics | Forecasts future customer behaviors based on historical data. | Churn prediction, sales forecasting, purchasing propensity modeling. | Enables proactive strategies and resource allocation. |
| Prescriptive Analytics | Recommends actions to optimize outcomes. | Personalized product recommendations, campaign optimization. | Drives tailored actions and enhances decision-making. |
Real-World CRM Analytics Examples
CRM analytics is widely implemented across diverse industries, driving tangible results in sales, marketing, customer service, and retention. Here are several practical examples demonstrating its impact:
- Retailers leveraging predictive analytics to stock popular products and optimize inventory.
- Banks using churn prediction models to identify high-risk customers and deploy retention offers.
- Healthcare providers segmenting patients for targeted outreach and personalized care plans.
- Telecommunications firms analyzing customer usage data to offer upsell and cross-sell opportunities.
- E-commerce platforms measuring campaign ROI and adjusting strategies in real time.
In the retail sector, for example, CRM analytics platforms analyze purchase histories and seasonal trends to anticipate demand spikes, allowing companies to maintain optimal inventory levels and reduce stockouts. Financial institutions utilize advanced models to assess customer attrition risk, flagging accounts likely to close and enabling tailored retention campaigns. In healthcare, segmentation models group patients by risk factors or care needs, supporting preventative outreach and improving patient outcomes.
Customer Segmentation Using CRM Analytics
Customer segmentation is a foundational use case for CRM analytics, enabling businesses to divide their customer base into distinct groups based on behaviors, preferences, or demographics. This approach allows for highly targeted marketing strategies and personalized engagement.
| Segment Criteria | Data Sources | Outcome | Practical Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics (age, income, location) | CRM profiles, survey responses | Tailored content and offers | Regional promotions for specific age groups |
| Purchase History | Transaction records, loyalty programs | Product recommendations | Upselling/cross-selling campaigns |
| Engagement Levels | Email opens, site visits, social interactions | Re-engagement or loyalty initiatives | Targeted win-back emails for inactive users |
| Customer Value | Revenue data, CLV analysis | Premium service tiers | Exclusive benefits for high-value customers |
A leading e-commerce company used CRM analytics to segment its customer base by purchase frequency and average order value. By identifying frequent, high-spending customers, the business launched VIP loyalty programs and personalized rewards, resulting in higher retention and increased customer advocacy. Another example involves a telecom provider segmenting subscribers based on data usage patterns, enabling tailored offers for heavy users and cost-saving plans for light users.
Sales Forecasting and Opportunity Analysis
Accurate sales forecasting is crucial for setting realistic targets and allocating resources efficiently. CRM analytics significantly enhances the accuracy of sales predictions and uncovers new revenue opportunities by analyzing historical sales data, current pipeline status, and market trends.
By feeding historical sales data into predictive models, organizations can forecast future sales with greater precision. These insights help businesses identify emerging opportunities, prioritize leads, and optimize sales strategies for better results.
- Regression analysis for trend forecasting
- Machine learning models for win probability and lead scoring
- Opportunity stage tracking within CRM platforms
- Pipeline visualization and scenario planning tools
- AI-powered recommendation engines for upsell/cross-sell
For example, a SaaS company used CRM analytics to analyze deal progression through the pipeline, identifying bottlenecks where deals commonly stalled. By retraining sales teams and refining lead qualification processes, they improved close rates and reduced sales cycle times.
Churn Prediction and Retention Strategies
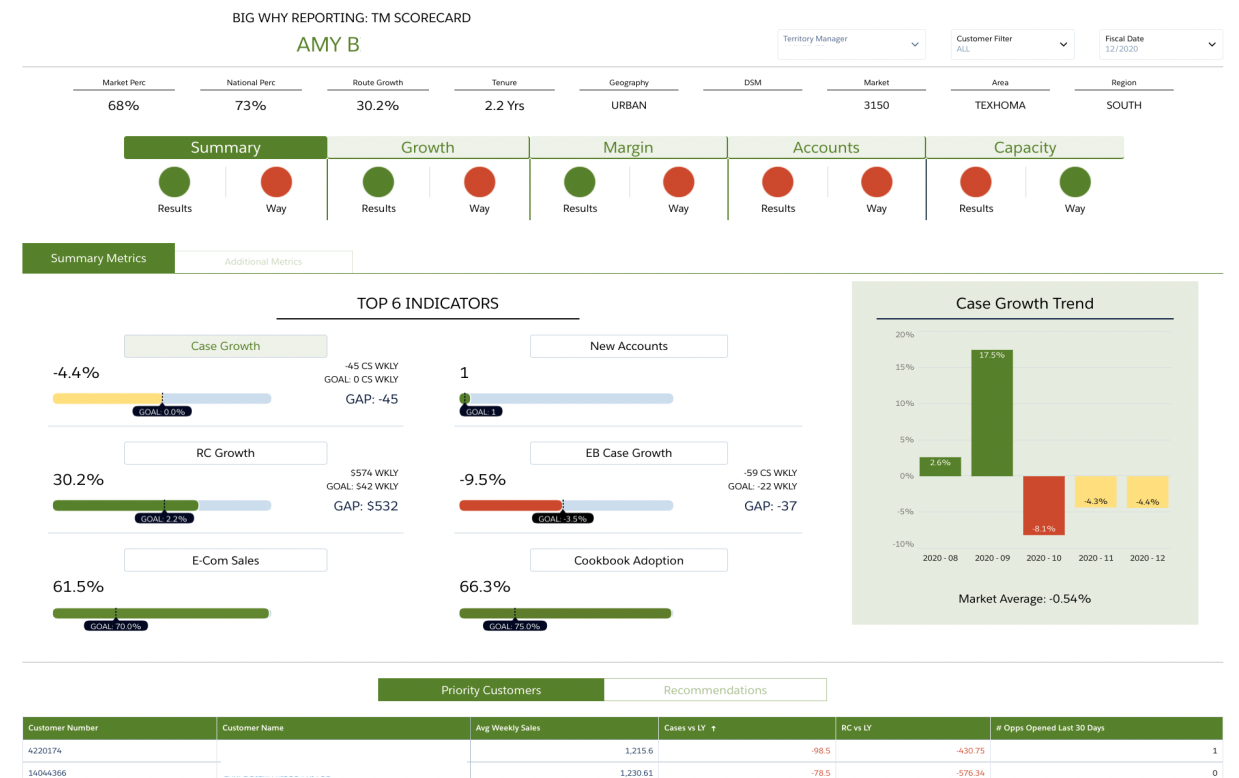
Predicting customer churn is a primary focus for many organizations seeking sustainable growth. CRM analytics empowers businesses to proactively identify customers at risk of leaving, enabling the implementation of strategic retention initiatives.
| Method | Data Used | Implementation Steps | Measured Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Churn Risk Scoring | Usage frequency, support tickets, purchase history | Develop model, assign risk scores, flag at-risk customers | Reduced churn rates by up to 20% |
| Personalized Outreach | Communication history, customer preferences | Segment at-risk customers, deploy targeted offers | Increased retention among high-value segments |
| Win-Back Campaigns | Inactive account data, last purchase date | Automate email or SMS re-engagement | Reactivation of 10–15% lapsed users |
A subscription service provider utilized predictive modeling to assign churn risk scores to all accounts. High-risk customers received proactive outreach—such as exclusive discounts or personalized support—resulting in a measurable decrease in churn over subsequent quarters. Another company implemented automated win-back campaigns based on inactivity data, leading to a notable recovery in customer reactivations.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) Analysis
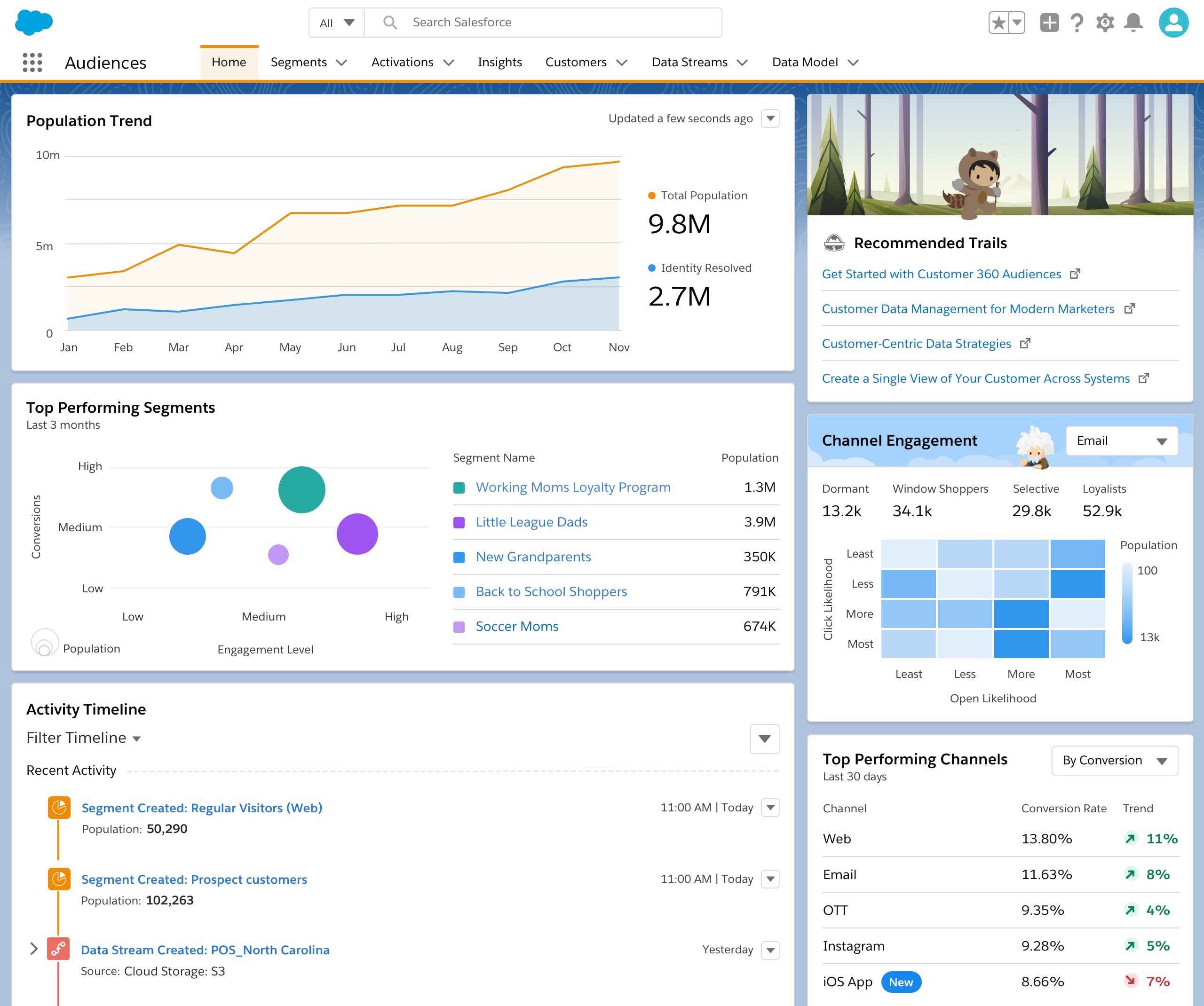
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) analysis is a critical CRM analytics function that estimates the total revenue a customer will generate over their relationship with a business. Understanding CLV helps companies allocate marketing budgets, prioritize service efforts, and devise differentiated loyalty strategies.
Scenario: A fashion retailer calculates CLV by combining average purchase value, frequency of purchases, and customer lifespan. By identifying high-CLV customers, the retailer invests more in retention activities for this segment, such as personalized recommendations and early access to new collections, driving higher profitability and long-term loyalty.
Scenario: A SaaS provider segments users into tiers based on predicted CLV. The company offers advanced support and features to high-value users, while automating onboarding for lower-tier customers, optimizing resource allocation.
Practical applications of CLV insights include targeting top-value customers with exclusive rewards, focusing retention marketing on profitable segments, and informing product development based on feedback from high-CLV users. Businesses routinely use CLV analysis to justify investments in customer experience initiatives, knowing that increased satisfaction among valuable users leads to the greatest returns.
Campaign Performance Evaluation
CRM analytics provides detailed visibility into marketing campaign effectiveness, allowing businesses to track key performance indicators (KPIs) and adjust strategies for optimal outcomes. Analytics-driven insights reveal which campaigns generate the highest ROI and engagement, supporting data-backed decision-making.
| KPI | Measurement Technique | Data Source | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conversion Rate | Track leads generated to sales closed | CRM deal stages, analytics dashboards | Measures campaign effectiveness in driving sales |
| Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) | Total campaign spend divided by new customers acquired | Marketing spend reports, CRM new accounts | Assesses cost-efficiency of campaigns |
| Engagement Rate | Analyze clicks, opens, shares | Email marketing analytics, website data | Evaluates audience interaction with campaign assets |
| Return on Investment (ROI) | Compare revenue generated against costs | Sales data, campaign budgets | Determines overall profitability |
For instance, a global electronics brand used CRM analytics to track real-time campaign performance, discovering that certain email segments delivered above-average conversion rates. By reallocating budget to these high-performing segments and optimizing underperforming ones, the company achieved a 30% increase in campaign ROI within a quarter.
Personalization and Customer Experience Enhancement
Personalization is a major driver of customer satisfaction and loyalty. CRM analytics facilitates highly tailored interactions by leveraging deep data insights, resulting in more relevant communications and engaging experiences throughout the customer journey.
- Segment-based content delivery using behavioral data
- Dynamic product recommendations powered by predictive algorithms
- Personalized customer support based on interaction history
- Triggered communications aligned with lifecycle stages
For example, an online retailer uses analytics to recommend products based on browsing and purchase history, leading to higher average order values and improved customer retention. In the banking sector, personalized loan offers and targeted financial advice are delivered through CRM analytics, increasing customer satisfaction and engagement. Support teams also rely on analytics to anticipate customer needs and resolve issues faster, enhancing the service experience at every touchpoint.
Integration of CRM Analytics Tools
The effectiveness of CRM analytics is closely tied to the capabilities of the tools and platforms employed. Leading CRM analytics solutions offer a range of features and integration options to suit different business environments, from startups to enterprises.
| Tool Name | Key Features | Integration Options | Typical Users |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salesforce Einstein Analytics | AI-powered predictions, dashboard visualizations, trend analysis | Native Salesforce integration, third-party apps via APIs | Large enterprises, sales & marketing teams |
| Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Insights | Unified customer profiles, segmentation, actionable insights | Microsoft ecosystem, Azure connectors, API integrations | Mid-to-large businesses, customer service teams |
| Zoho CRM Analytics | Custom reports, pipeline analytics, sales forecasting | Zoho suite, REST APIs, Zapier | SMBs, sales-driven organizations |
| HubSpot CRM Analytics | Lifecycle tracking, marketing attribution, automation workflows | HubSpot platform, API, popular marketing apps | Startups, digital marketers |
When selecting a CRM analytics tool, businesses should consider their existing technology stack, scalability needs, data integration requirements, and the user-friendliness of the platform. Choosing the right tool ensures seamless adoption, actionable insights, and maximum return on investment for CRM analytics initiatives.
Conclusion
Exploring crm analytics examples reveals the incredible value these strategies bring to businesses eager to thrive in competitive markets. By leveraging deep data analysis and smart segmentation, companies not only improve results but also foster lasting customer relationships and drive innovation across their organizations.
Clarifying Questions
What types of businesses benefit most from CRM analytics examples?
Any business aiming to improve customer interactions and drive growth can benefit, but industries like retail, finance, healthcare, and e-commerce often see the most immediate impact due to high customer engagement and data availability.
How can CRM analytics examples help reduce customer churn?
CRM analytics can identify early warning signs of customer dissatisfaction, allowing businesses to proactively engage at-risk customers and implement targeted retention strategies before they leave.
Are CRM analytics examples only useful for large companies?
No, businesses of all sizes can use CRM analytics. Many tools are scalable and offer functionalities that fit small and medium-sized enterprises as well as large corporations.
What data sources are typically used in CRM analytics examples?
Common data sources include customer profiles, transaction histories, support tickets, website activity, email interactions, and social media engagements.
How quickly can a business see results after implementing CRM analytics?
Timelines vary, but many businesses start seeing measurable improvements in customer segmentation, sales forecasting, and marketing performance within a few months of active use.