crm and analytics unlocking smarter business growth
crm and analytics sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, diving right into how businesses can transform their relationships with customers through data-driven insights and innovative technology. In today’s competitive market, understanding customers is more than a necessity—it’s a strategic advantage, and crm and analytics are at the forefront of this evolution.
From tracking customer interactions to forecasting sales trends, crm and analytics empower organizations to make informed decisions at every level. By combining robust customer relationship management with powerful analytical tools, businesses can uncover hidden opportunities, fine-tune marketing strategies, and deliver truly personalized experiences that foster loyalty and drive growth.
CRM and Analytics Integration in Modern Business
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and analytics have become critical pillars in contemporary business strategy, enabling organizations to better understand, engage, and serve their customers. While CRM focuses on managing interactions and fostering relationships throughout the customer lifecycle, analytics provides actionable insights derived from data to drive informed decision-making. The convergence of these two domains has transformed how businesses approach customer engagement, sales, and service delivery.
Overview of CRM and Analytics

CRM systems were first introduced as digital tools to store customer information and manage interactions, primarily replacing outdated manual record-keeping methods. Over time, these systems evolved into integrated platforms supporting marketing, sales, and customer service functions. The addition of analytics capabilities marked a new era, allowing businesses to collect, process, and interpret vast amounts of customer data for strategic advantage. When CRM and analytics are combined, organizations gain a holistic view of their customers and the ability to make evidence-based decisions that enhance customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Key Features of Modern CRM Systems
Modern CRM platforms are equipped with a diverse set of features designed to streamline processes and elevate customer engagement. These features go beyond simple contact management, incorporating sophisticated tools for data analysis, automation, and workflow optimization. The following table Artikels essential CRM features, their descriptions, associated business benefits, and industry examples:
| Feature | Description | Business Benefit | Industry Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead Management | Tracks and manages potential customers through the sales funnel. | Increases sales conversion rates and prioritizes valuable prospects. | B2B SaaS companies qualifying enterprise leads. |
| Customer Segmentation | Divides customers into targeted groups based on demographics or behavior. | Enables personalized marketing and higher engagement. | Retailers segmenting shoppers for seasonal campaigns. |
| Workflow Automation | Automates repetitive tasks and follow-ups within the CRM. | Boosts team efficiency and reduces human error. | Insurance agencies automating policy renewal reminders. |
| Integrated Communication Tools | Centralizes email, chat, and call history for each customer. | Improves service consistency and quick access to information. | Customer support centers handling ticket resolutions. |
These features collectively empower teams to understand customer needs at a granular level, resulting in more relevant interactions and long-term loyalty.
Integration of Analytics with CRM Platforms
Analytics functionalities are now deeply embedded within CRM platforms, enabling businesses to analyze customer data in real time and make strategic decisions with confidence. This integration supports a data-driven culture by allowing users to access analytics dashboards, generate reports, and visualize trends directly within the CRM environment.
Common Analytics Functionalities in CRM Platforms
Integrating analytics within CRM platforms unlocks a range of capabilities essential for business analysis and forecasting. Some of the primary analytics features include:
- Reporting Dashboards: Consolidate key metrics such as sales performance, campaign results, and customer activity into interactive visual summaries.
- Predictive Modeling: Utilizes historical data to forecast future behaviors, such as likelihood of purchase or risk of churn.
- Real-Time Data Visualization: Presents up-to-the-minute insights on customer interactions, enabling agile responses.
- Custom Analytics Workflows: Allows users to design specific analyses tailored to their team’s objectives.
Embedding analytics into CRM not only streamlines operations by reducing manual data transfers but also provides a unified platform for tracking customer journeys, optimizing marketing campaigns, and enhancing sales strategies.
Types of Analytics Used in CRM
The analytics embedded within CRM platforms can be broadly categorized into four types, each serving a distinct purpose in customer management. Businesses leverage these types to address different questions, from understanding what happened to determining optimal future actions.
| Analytics Type | Application | Data Requirement | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Descriptive Analytics | Summarizes historical customer data and interactions. | Transaction logs, interaction records. | Clear understanding of customer behavior trends. |
| Diagnostic Analytics | Explains reasons behind specific outcomes or behaviors. | Combined datasets, root cause analysis. | Identification of key drivers affecting performance. |
| Predictive Analytics | Forecasts future customer actions or preferences. | Historical data, machine learning models. | Proactive targeting and churn reduction. |
| Prescriptive Analytics | Recommends best actions based on predictive outcomes. | Predictive outputs, optimization algorithms. | Informed decision-making and improved ROI. |
Real-world use cases include using descriptive analytics to identify high-value customer segments, diagnostic analytics to uncover why a marketing campaign underperformed, predictive analytics to anticipate which leads will convert, and prescriptive analytics to suggest personalized offers that maximize engagement.
Benefits of Using CRM with Analytics in Business
When CRM and analytics work in tandem, the impact on business performance is substantial. Organizations benefit from increased customer retention, tailored marketing strategies, and refined sales forecasts. The integration supports a proactive approach, allowing businesses to anticipate customer needs and deliver personalized experiences at scale.
A retail company struggling with frequent customer churn implemented analytics-driven CRM. By analyzing browsing and purchase behavior, the company identified at-risk customers and sent targeted loyalty offers. Within six months, their retention rate improved by 25%, and average revenue per user increased significantly.
Prior to adopting analytics, the company relied on generic outreach and faced diminishing returns. After deployment, every customer interaction became data-informed, resulting in more meaningful engagement and measurable business growth.
Data Sources and Data Quality in CRM Analytics
Effective CRM analytics relies on diverse internal and external data sources, each contributing unique perspectives on customer behavior. Common internal sources include sales transactions, customer support logs, website activity, and email campaign results. External sources may involve social media data, demographic information from third-party providers, and industry benchmarks.
Ensuring data quality is vital for reliable analytics. Inaccurate, duplicate, or inconsistent data can lead to misleading insights and poor business decisions. Regular data cleansing, validation, and consistency checks are essential to maintain high standards.
- Establish clear data entry guidelines for all CRM users.
- Automate data deduplication and error detection processes.
- Integrate CRM with trusted external data providers for enrichment.
- Conduct periodic audits to identify and address data inconsistencies.
- Utilize data validation rules to minimize human errors during entry.
Adhering to these practices safeguards the value and accuracy of analytics outcomes, supporting data-driven business growth.
Common Challenges in CRM and Analytics Adoption
Organizations often encounter several challenges when adopting and integrating CRM analytics, from data silos and integration complexities to resistance among end users. Addressing these obstacles is necessary to unlock the full potential of CRM analytics.
| Challenge | Impact | Solution | Priority Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Silos | Fragmented customer data limits comprehensive analysis. | Implement centralized data integration strategies. | High |
| Integration Complexity | Technical difficulties in connecting CRM with analytics tools. | Adopt platforms with strong API and integration support. | Medium |
| User Adoption | Lack of engagement hinders successful implementation. | Invest in training and change management programs. | High |
| Data Quality Issues | Poor quality data results in unreliable analytics. | Establish robust data governance and cleansing routines. | Medium |
Overcoming these challenges involves fostering interdepartmental collaboration, leveraging agile IT solutions, and prioritizing user-centric change management.
Innovative Applications and Trends in CRM Analytics

The CRM analytics landscape is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer expectations. Emerging trends are reshaping how organizations leverage data for customer management and engagement.
The latest innovations include:
- AI-Driven Insights: Using machine learning algorithms to identify patterns and recommend actions autonomously. For instance, financial services firms use AI to flag fraudulent activity and suggest preventive steps.
- Customer Journey Mapping: Integrating multi-channel data to visualize and optimize every touchpoint in the customer lifecycle. Retailers employ journey analytics to streamline the path from product discovery to purchase.
- Omnichannel Analytics: Combining data from web, mobile, social, and in-store interactions to provide a unified customer profile. Hospitality brands use omnichannel insights to tailor guest experiences across booking, check-in, and post-stay engagement.
- Voice and Sentiment Analysis: Applying natural language processing to analyze customer feedback from calls and messages, enabling real-time service improvements.
- Automated Personalization Engines: Delivering hyper-targeted offers and content based on predictive analytics, as seen in streaming services recommending shows based on individual viewing patterns.
Each of these advancements demonstrates how powerful analytics capabilities are redefining CRM strategies and driving superior business results.
Best Practices for Implementing CRM Analytics
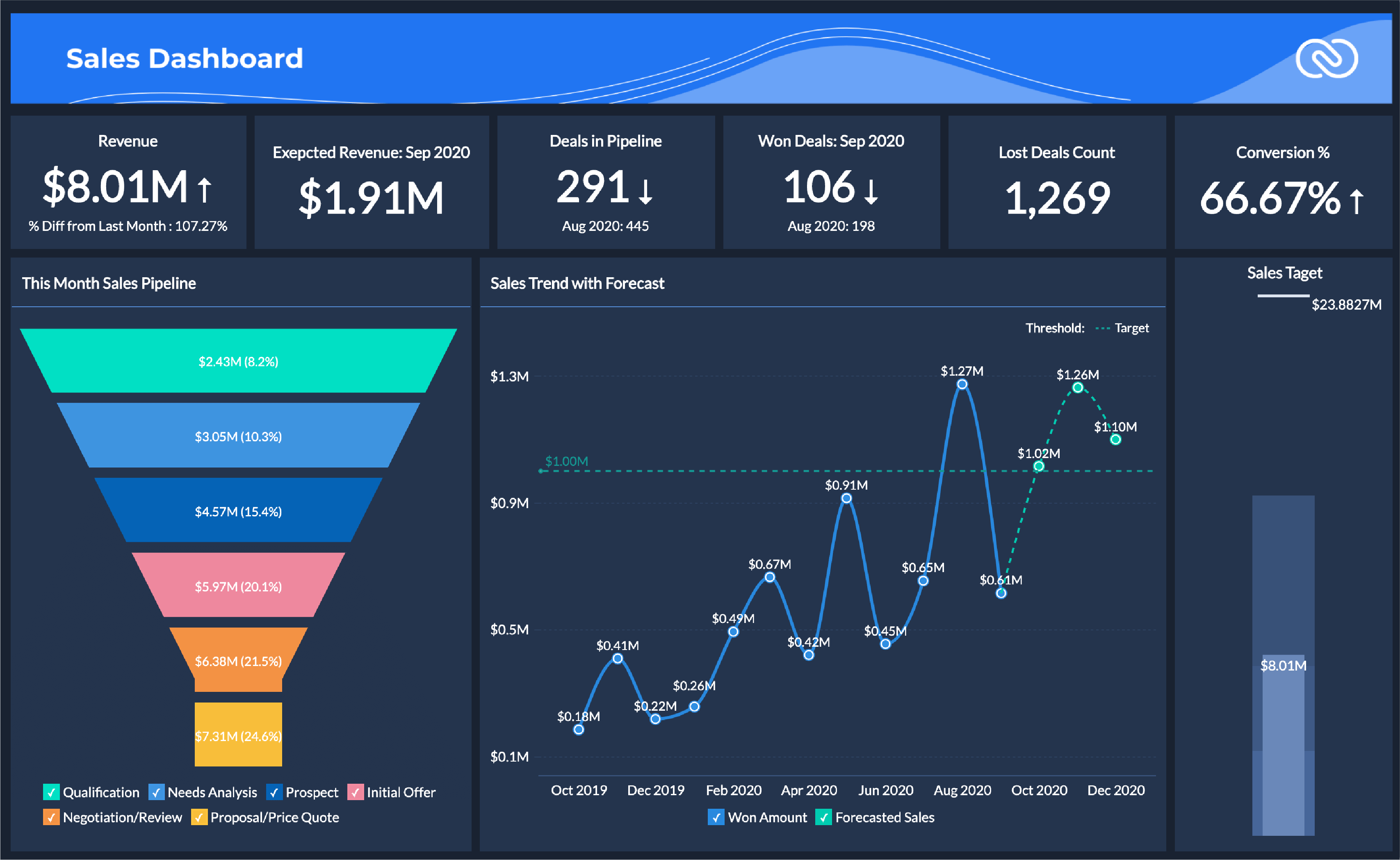
The process of implementing analytics within CRM environments requires a structured approach to ensure success. Businesses should focus on cross-functional collaboration, technical readiness, and continuous improvement.
| Stage | Key Actions | Responsible Team | Expected Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assessment & Planning | Evaluate needs, define objectives, select CRM analytics stack. | Leadership, IT, Data Science | Clear project scope and alignment with business goals. |
| Data Preparation | Cleanse data, integrate sources, ensure data quality. | IT, Data Management | Reliable, unified data foundation. |
| Implementation | Configure CRM, embed analytics, establish workflows. | IT, CRM Administrators | Operational CRM analytics platform. |
| User Training & Adoption | Conduct training, set KPIs, incentivize usage. | HR, CRM Champions | High user engagement and effective utilization. |
| Ongoing Optimization | Monitor performance, refine analytics, scale solutions. | Analytics, Business Units | Continuous improvement and ROI growth. |
Key techniques include developing detailed training modules, regularly reviewing KPIs, and maintaining a feedback loop for system enhancements and evolving business needs.
Real-World Case Studies of CRM and Analytics Success
Numerous organizations have achieved transformative outcomes by integrating CRM with analytics. The case studies below illustrate the tangible benefits realized across different industries:
- Retail Chain Optimization: A global retailer faced declining sales due to ineffective promotions. By leveraging CRM analytics to segment customers and predict product preferences, they tailored promotions and increased sales by 18% in one quarter. The use of predictive modeling guided inventory planning, reducing stockouts and excess inventory.
- Financial Services Customer Retention: A major bank dealt with high attrition among premium account holders. Combining CRM data with sentiment analysis and predictive churn models, the bank proactively offered personalized incentives, decreasing churn rates by 30% and boosting customer satisfaction scores.
- Healthcare Patient Engagement: A hospital network implemented CRM analytics to track patient interactions and automate appointment reminders. Prescriptive analytics identified patients at risk of missing appointments, allowing staff to intervene early. Appointment adherence improved, leading to better health outcomes and operational efficiency.
- B2B Sales Acceleration: A technology provider streamlined its sales pipeline using workflow automation and real-time analytics dashboards. Sales cycles shortened by 20%, and win rates improved as sales teams focused on high-potential prospects identified through lead scoring models.
These examples underscore the pivotal role of analytics-enabled CRM in solving industry-specific challenges and delivering measurable business value.
Last Point: Crm And Analytics
In summary, crm and analytics are reshaping the way businesses connect with their customers, making every interaction more meaningful and impactful. By harnessing the combined power of these tools, organizations can stay ahead of the curve, unlock new value, and set themselves up for long-term success in an ever-changing landscape.
FAQ Overview
What is the main goal of integrating crm and analytics?
The main goal is to use customer data and insights to improve decision-making, optimize business processes, and personalize customer interactions for better engagement and retention.
Can small businesses benefit from crm and analytics?
Absolutely. Even small businesses can use crm and analytics to organize customer information, identify trends, and create targeted marketing campaigns that increase efficiency and growth.
Is specialized training needed to use crm and analytics tools?
Most modern crm and analytics platforms are user-friendly, but some training helps teams fully leverage advanced features and interpret data effectively.
How often should crm data be updated and analyzed?
Regular updates and continuous analysis are recommended to ensure data accuracy and stay responsive to customer needs. Many tools offer real-time updates and automated reporting to streamline this process.
What types of data are most valuable for crm analytics?
Customer profiles, sales transactions, support interactions, website behavior, and external demographic data are among the most valuable sources for gaining actionable insights.